高泽峰(Ze-Feng Gao)中国人民大学物理学院讲师 。中国人民大学青年英才。研究方向为量子物理数值方法、预训练模型压缩、AI辅助功能性晶体材料的发现与生成。基于矩阵乘积算符表示的神经网络、针对语音增强领域的模型压缩和小型化和面向预训练模型的轻量化微调与模型扩容三个方面,构建了基于矩阵乘积算符表示的理论方法。同时,应用人工智能方法辅助功能性新材料发现。已在本领域相关的国内外学术期刊和会议上发表论文二十余篇,涵盖ACL、NeurIPS、EMNLP、COLING等人工智能重要会议和National Science Review、Phys.Rev.Research等SCI重要期刊。其中,基于矩阵乘积算符实现预训练模型的过参数化过程的工作获得ACL2023最佳论文提名。研究成果被来自剑桥大学、斯坦福大学、Meta公司等科研机构的领域专家引用。近三年主持基金7项,包括国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目、国家自然科学基金面上项目、国家自然科学基金重点项目(子课题)、国家重点研发计划“物态调控”专项项目(子课题)与横向项目3项。 Email: zfgao@ruc.edu.cn GitHub / Google Scholar / DBLP / |

|
教育经历 |
工作经历 |
邀请报告 |
科研项目 |
教授课程 |
科研论文
2025 |
|
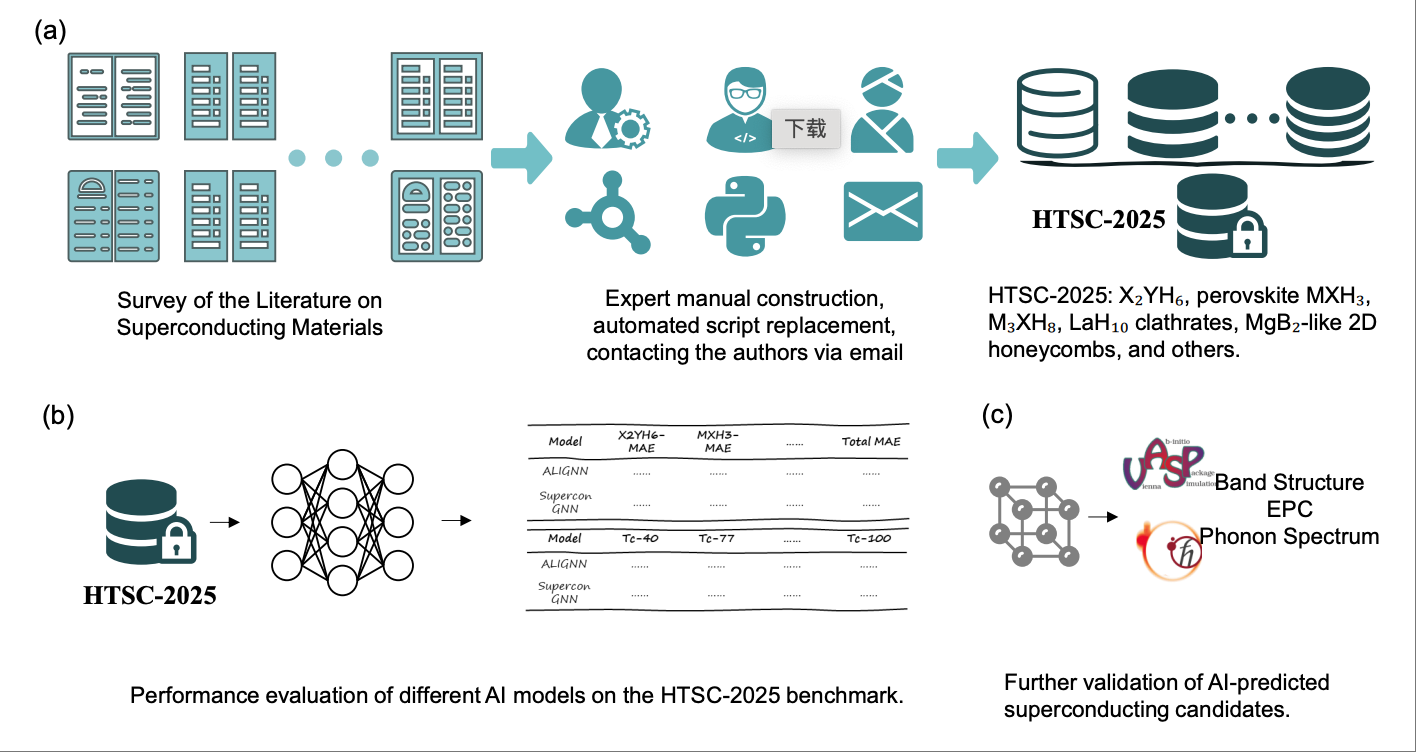
HTSC-2025: A Benchmark Dataset of Ambient-Pressure High-Temperature Superconductors for AI-Driven Critical Temperature PredictionXiao-Qi Han, Ze-Feng Gao#, Xin-De Wang, Zhenfeng Ouyang, Peng-Jie Guo, Zhong-Yi Lu Arxiv, 2025 paper / arxiv / code / In this work, we present the HTSC-2025, an ambient-pressure high-temperature superconducting benchmark dataset. This comprehensive compilation encompasses theoretically predicted superconducting materials discovered by theoretical physicists from 2023 to 2025 based on BCS superconductivity theory, including the renowned XYH6 system, perovskite MXH3 system, M3XH8 system, cage-like BCN-doped metal atomic systems derived from LaH structural evolution, and two-dimensional honeycomb-structured systems evolving from MgB2. |
|
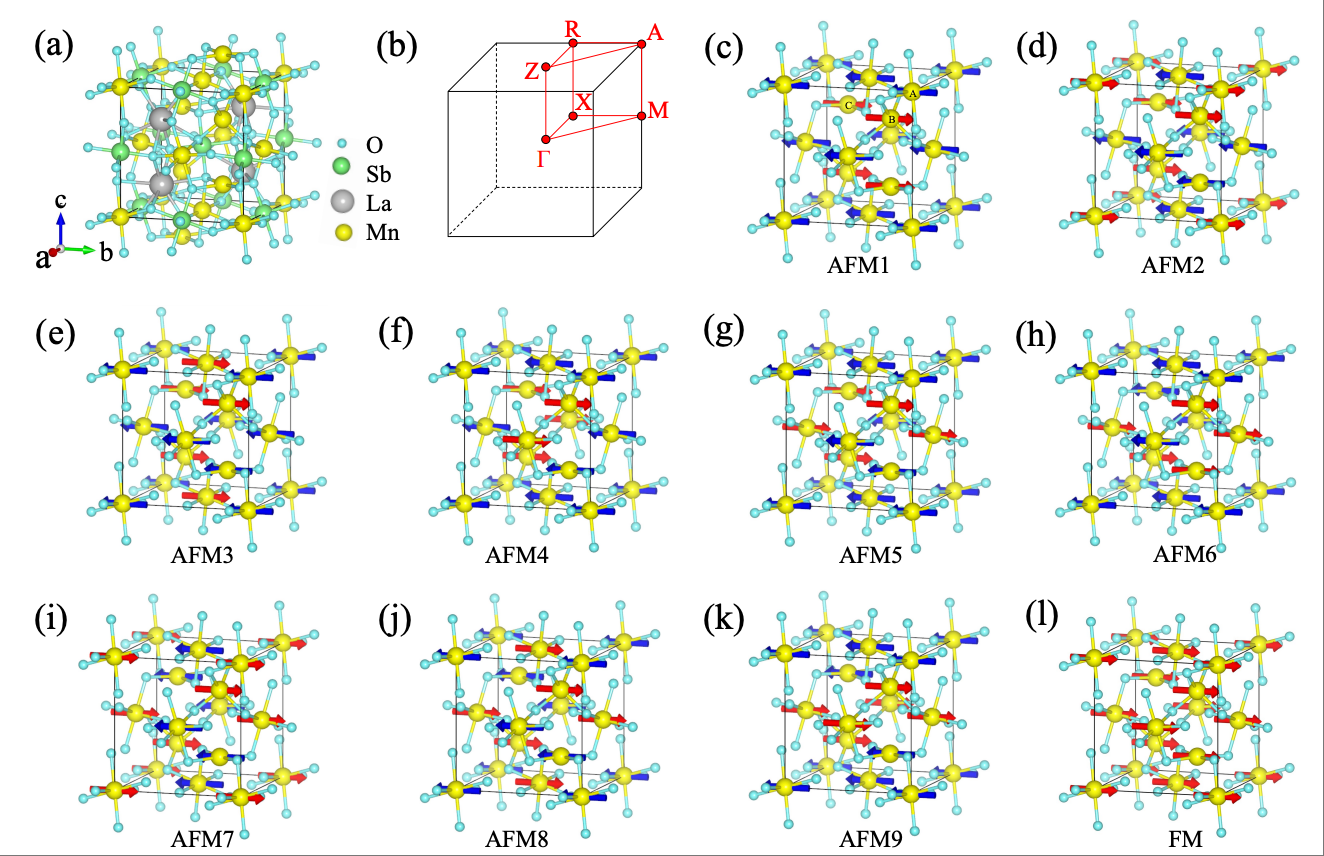
Unconventional compensated magnetic material LaMn2SbO6Xiao-Yao Hou, Ze-Feng Gao, Huan-Cheng Yang, Peng-Jie Guo, Zhong-Yi Lu Chinese Physics Letter, 2025 paper / arxiv / link / In this study, based on symmetry analysis and the first-principles electronic structure calculations, we predict that LaMn2SbO6 is a unconventional compensated magnetic semiconductor. Given that the Mn ions at opposite spin lattice cannot be connected by any symmetry, the spin splitting in LaMn2SbO6 is isotropic. More importantly, LaMn2SbO6 has already been synthesized experimentally, and its magnetic structure has been confirmed by neutron scattering experiments. |
|
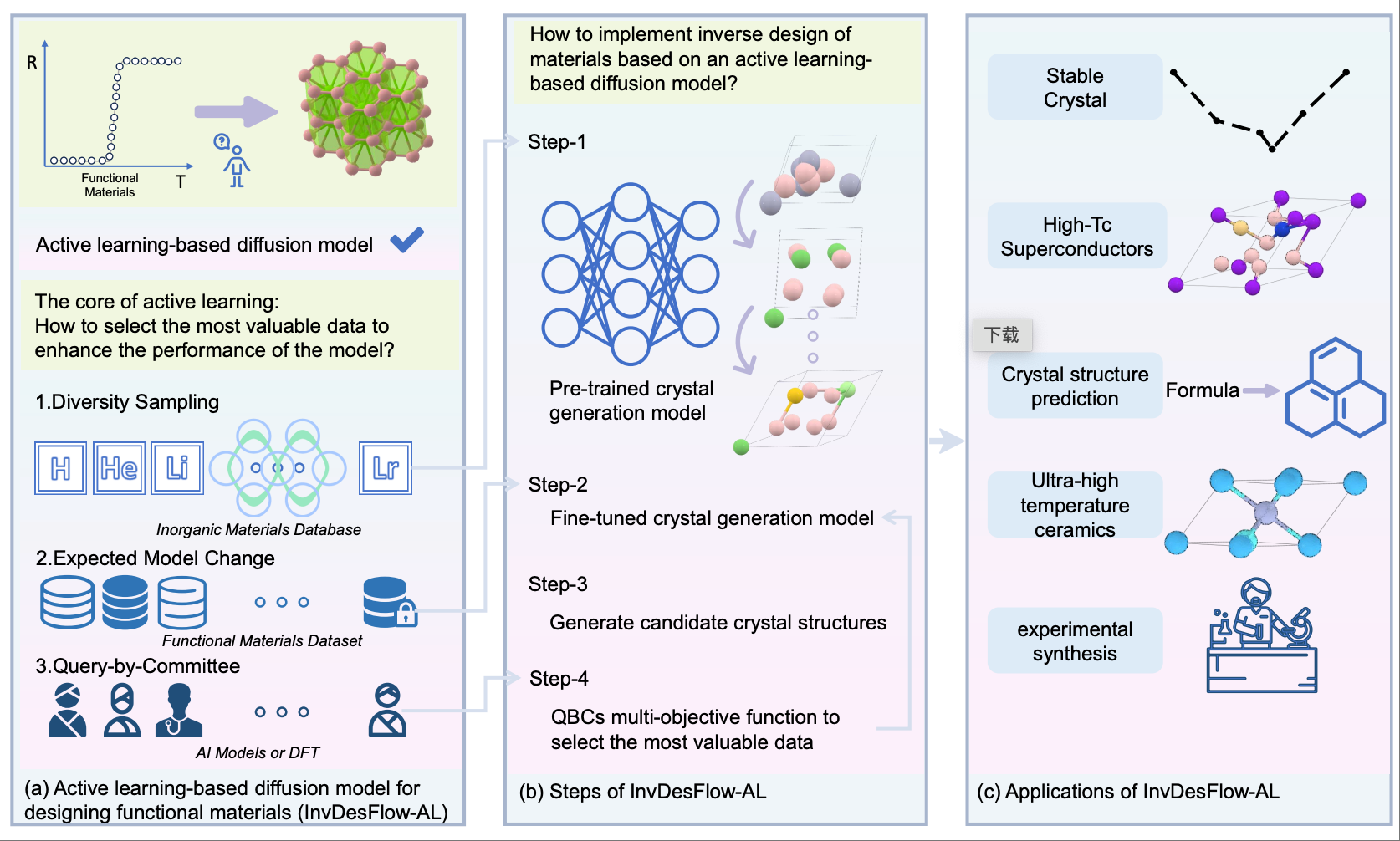
InvDesFlow-AL: Active Learning-based Workflow for Inverse Design of Functional MaterialsXiao-Qi Han, Peng-Jie Guo, Ze-Feng Gao#, Hao Sun#,Zhong-Yi Lu# Arxiv, 2025 paper / arxiv / code / In this work, we propose a novel inverse material design generative framework called InvDesFlow-AL, which is based on active learning strategies. This framework can iteratively optimize the material generation process to gradually guide it towards desired performance characteristics. In terms of crystal structure prediction, the InvDesFlow-AL model achieves an RMSE of 0.0423 {\AA}, representing an 32.96% improvement in performance compared to exsisting generative models. |
|
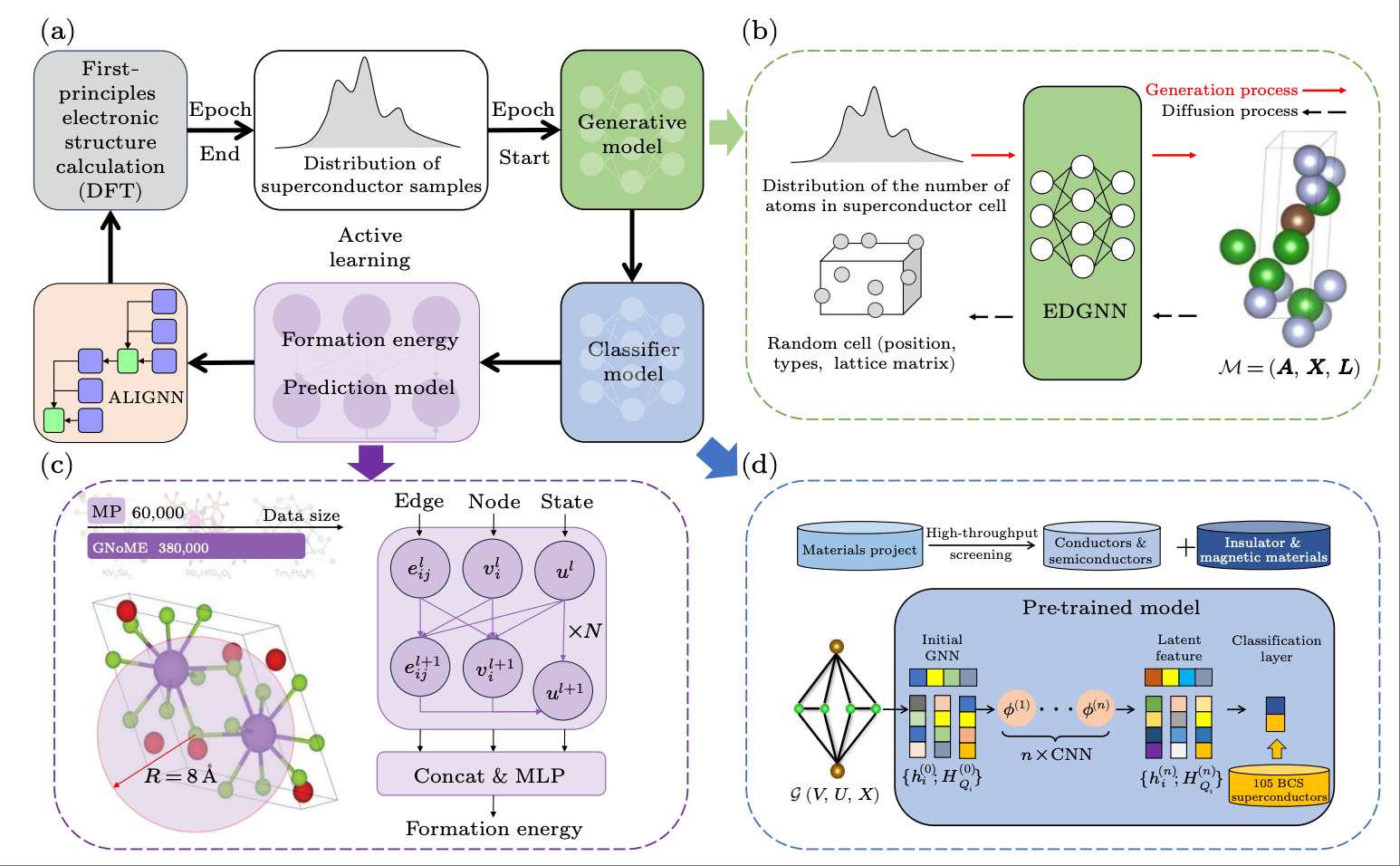
InvDesFlow: An AI-driven materials inverse design workflow to explore possible high-temperature superconductorsXiao-Qi Han, Zhenfeng Ouyang, Peng-Jie Guo, Hao Sun, Ze-Feng Gao#, Zhong-Yi Lu# Chinese Physics Letter, 2025 paper / code / link / We develop InvDesFlow, an artificial intelligence (AI)-driven materials inverse design workflow that integrates deep model pre-training and fine-tuning techniques, diffusion models, and physics-based approaches (e.g., first-principles electronic structure calculation) for the discovery of high-Tc superconductors. Utilizing InvDesFlow, we have obtained 74 thermodynamically stable materials with critical temperatures predicted by the AI model to be Tc ≥ 15 K based on a very small set of samples. Notably, these materials are not contained in any existing dataset. |
|
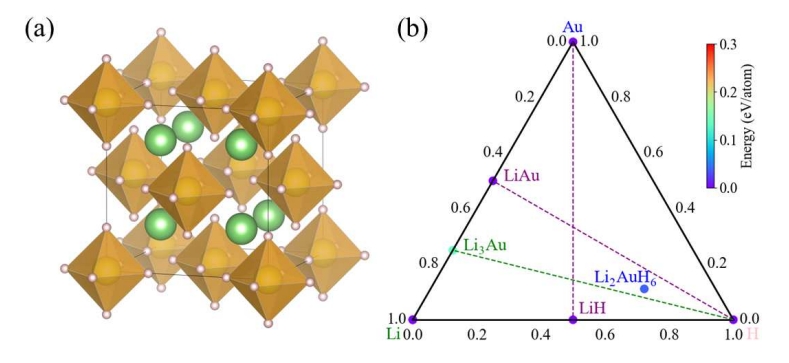
High-temperature superconductivity in Li2AuH6 mediated by strong electron-phonon coupling under ambient pressureZhenfeng Ouyang, Bo-Wen Yao, Xiao-Qi Han, Peng-Jie Guo, Ze-Feng Gao#, Zhong-Yi Lu# Physics Review B (Letter), 2025 paper / arxiv / code / link / We used our developed AI search engine~(InvDesFlow) to perform extensive investigations regarding ambient stable superconducting hydrides. A cubic structure Li2AuH6 with Au-H octahedral motifs is identified to be a candidate. After performing thermodynamical analysis, we provide a feasible route to experimentally synthesize this material via the known LiAu and LiH compounds under ambient pressure. The further first-principles calculations suggest that Li2AuH6 shows a high superconducting transition temperature (Tc) ∼ 140 K under ambient pressure. |
|
AI-accelerated Discovery of Altermagnetic MaterialsZe-Feng Gao*, Shuai Qu*, Bocheng Zeng*, Yang Liu, Ji-Rong Wen, Hao Sun#, Peng-Jie Guo#, Zhong-Yi Lu# National Science Review, 2025 paper / arxiv / code / link / In this paper, we successfully discovered 50 new altermagnetic materials that cover metals, semiconductors, and insulators confirmed by the first-principles electronic structure calculations. The wide range of electronic structural characteristics reveals that various novel physical properties manifest in these newly discovered altermagnetic materials, e.g., anomalous Hall effect, anomalous Kerr effect, and topological property. |
|
2024 |
|
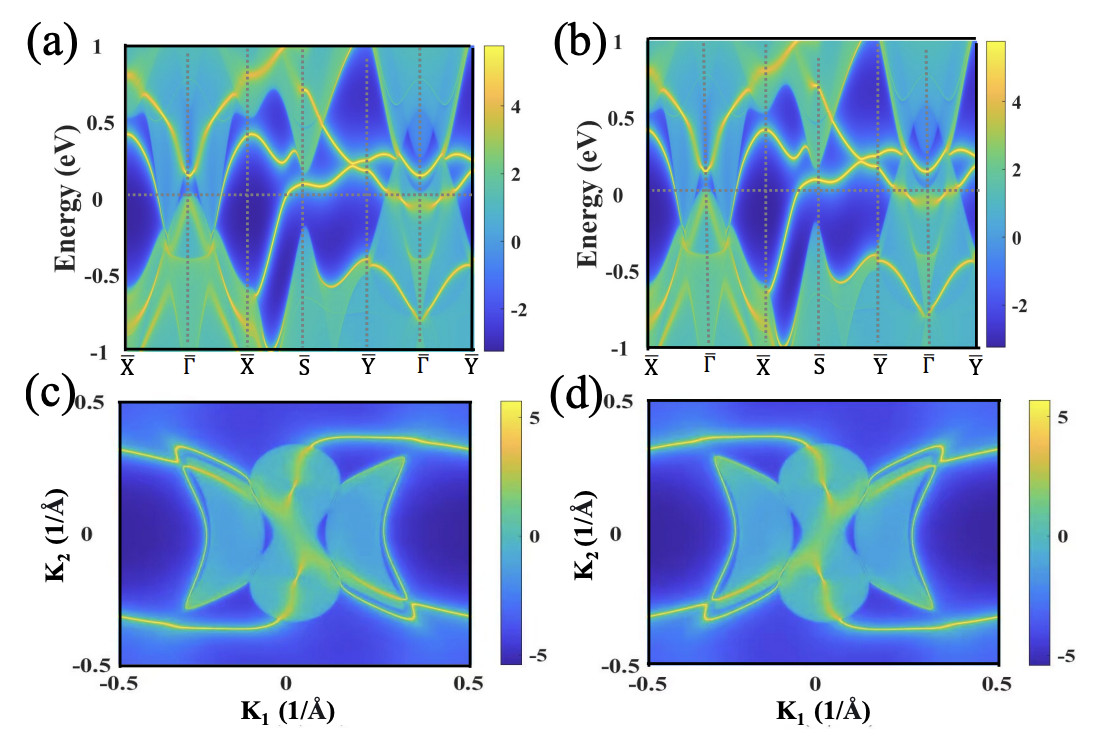
Type-II Dirac nodal chain semimetal CrB4Xiao-Yao Hou, Ze-Feng Gao, Peng-Jie Guo#, Jian-Feng Zhang, Zhong-Yi Lu# Arxiv, 2024 paper / arxiv / In this study, based on symmetry analysis and the first-principles electronic structure calculations, we predict that CrB4 is an ideal type-II Dirac nodal chain semimetal protected by the mirror symmetry. Moreover, there are two nodal rings protected by both space-inversion and time-reversal symmetries in CrB4. More importantly,in CrB4 the topologically protected drumhead surface states span the entire Brillouin zone at the Fermi level. |
|
AI-driven inverse design of materials: Past, present and futureXiao-Qi Han, Xin-De Wang, Meng-Yuan Xu, Zhen Feng, Bo-Wen Yao, Peng-Jie Guo, Ze-Feng Gao#, Zhong-Yi Lu# Chinese Physics Letter, 2024 paper / arxiv / link / In this survey, we look back on the latest advancements in AI-driven inverse design of materials by introducing the background, key findings, and mainstream technological development routes. In addition, we summarize the remaining issues for future directions. This survey provides the latest overview of AI-driven inverse design of materials, which can serve as a useful resource for researchers. |
|
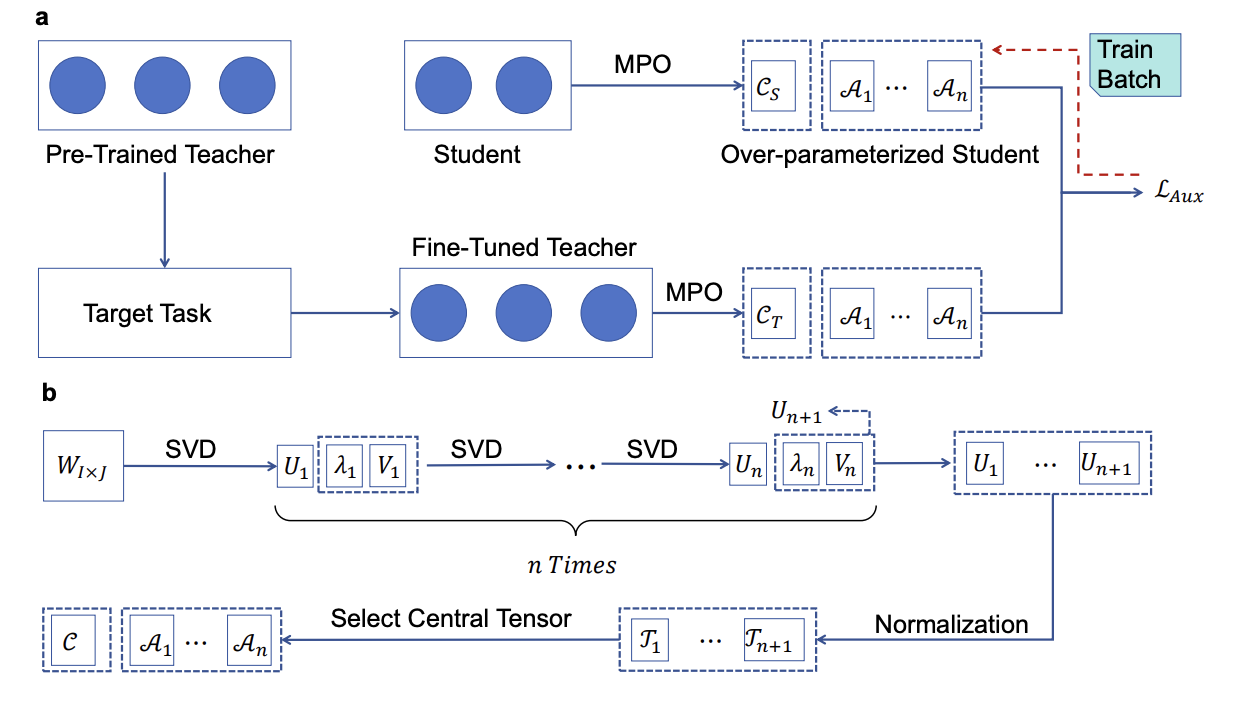
Over-parameterized Student Model via Tensor Decomposition Boosted Knowledge DistillationYu-Liang Zhan, Zhong-Yi Lu, Hao Sun#, Ze-Feng Gao# 38th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024), 2024 paper / arxiv / code / link / In this paper, we scale up the parameters of the student model during training, to benefit from over-parameterization without increasing the inference latency. In particular, we propose a tensor decomposition strategy that effectively over-parameterizes the relatively small student model through an efficient and nearly lossless decomposition of its parameter matrices into higher-dimensional tensors. |
|
Crystal valley Hall effectChao-Yang Tan, Ze-Feng Gao, Huan-Cheng Yang, Zheng-Xin Liu, Kai Liu, Peng-Jie Guo#, Zhong-Yi Lu# Arxiv, 2024 paper / arxiv / In this paper, based on symmetry analysis and the first-principles electronic structure calculations, we demonstrate that the vally Hall effect without time-reversal symmetry can be realized in two-dimensional altermagnetic materials Fe2WSe4 and Fe2WS4. Due to crystal symmetry required, the vally Hall effect without time-reversal symmetry is called crystal vally Hall effect. In addition, under uniaxial strain, both monolayer Fe2WSe4 and Fe2WS4 can realize piezomagnetic effect. |
|
YuLan: An Open-source Large Language ModelYutao Zhu, Kun Zhou, Kelong Mao, Wentong Chen, Yiding Sun, Zhipeng Chen, Qian Cao, Yihan Wu, Yushuo Chen, Feng Wang, Lei Zhang, Junyi Li, Xiaolei Wang, Lei Wang, Beichen Zhang, Zican Dong, Xiaoxue Cheng, Yuhan Chen, Xinyu Tang, Yupeng Hou, Qiangqiang Ren, Xincheng Pang, Shufang Xie, Wayne Xin Zhao, Zhicheng Dou, Jiaxin Mao, Yankai Lin, Ruihua Song, Jun Xu, Xu Chen, Rui Yan, Zhewei Wei, Di Hu, Wenbing Huang, Ze-Feng Gao, Yueguo Chen, Weizheng Lu, Ji-Rong Wen Arxiv, 2024 paper / arxiv / In this paper, we design a three-stage pre-training method to enhance YuLan’s overall capabilities. Subsequent phases of training incorporate instruction-tuning and human alignment, employing a substantial volume of high-quality synthesized data. To facilitate the learning of complex and long-tail knowledge, we devise a curriculum-learning framework throughout across these stages, which helps LLMs learn knowledge in an easy-to-hard manner. |
|
Do Emergent Abilities Exist in Quantized Large Language Models: An Empirical StudyPeiyu Liu, Zikang Liu, Ze-Feng Gao, Dawei Gao, Wayne Xin Zhao#,Yaliang Li, Bolin Ding, Ji-Rong Wen Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (COLING 2024), 2024 paper / arxiv / code / link / This work aims to investigate the impact of quantization on \emph{emergent abilities}, which are important characteristics that distinguish LLMs from small language models. Specially, we examine the abilities of in-context learning, chain-of-thought reasoning, and instruction-following in quantized LLMs. |
|
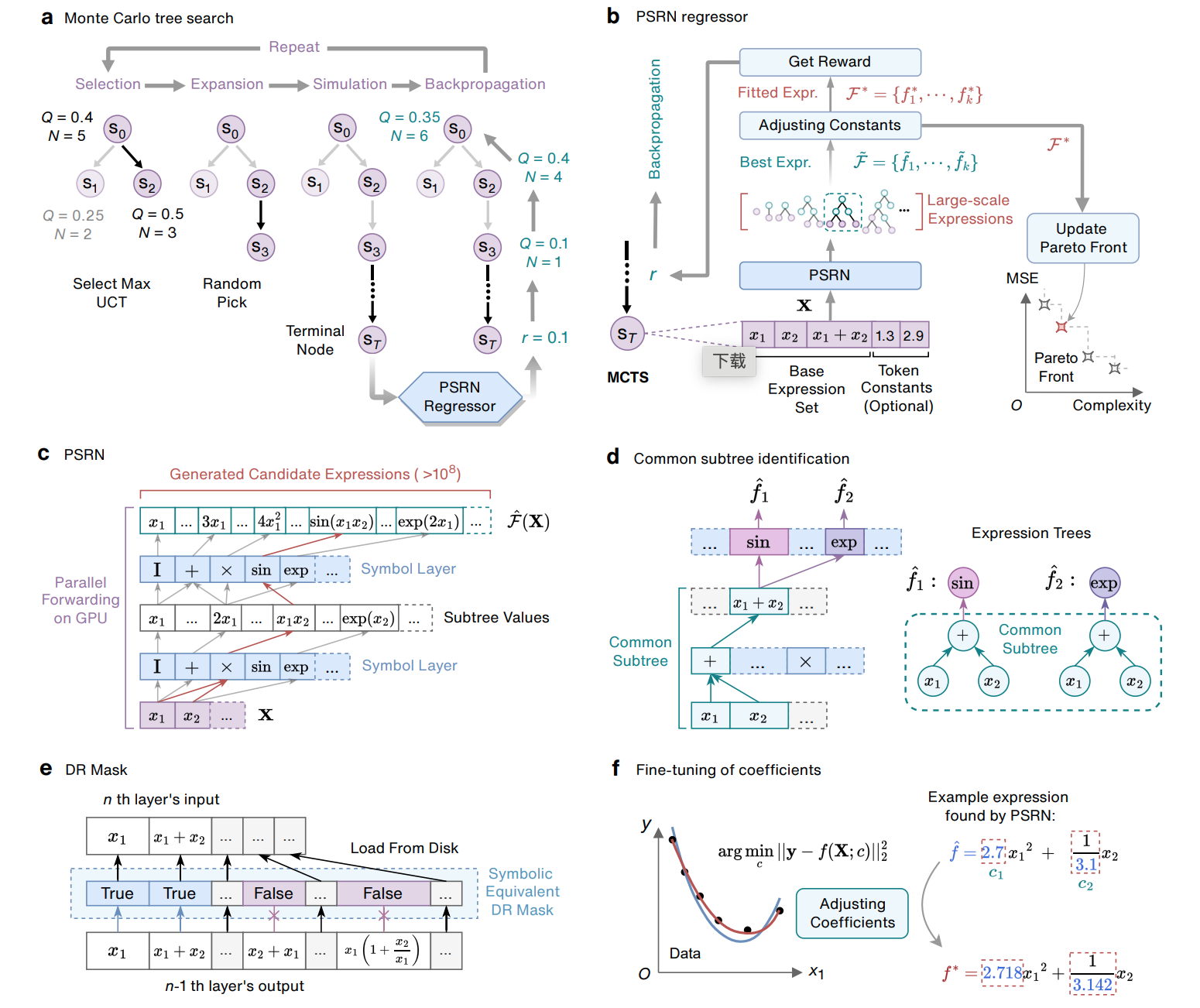
Discovering symbolic expressions with parallelized tree searchKai Ruan, Ze-Feng Gao, Yike Guo, Hao Sun#, Ji-Rong Wen, Yang Liu Arxiv, 2024 paper / arxiv / In this paper, we introduce a parallelized tree search (PTS) model to efficiently distill generic mathematical expressions from limited data. Through a series of extensive experiments, we demonstrate the superior accuracy and efficiency of PTS for equation discovery, which greatly outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline models on over 80 synthetic and experimental datasets (e.g., lifting its performance by up to 99% accuracy improvement and one-order of magnitude speed up). |
|
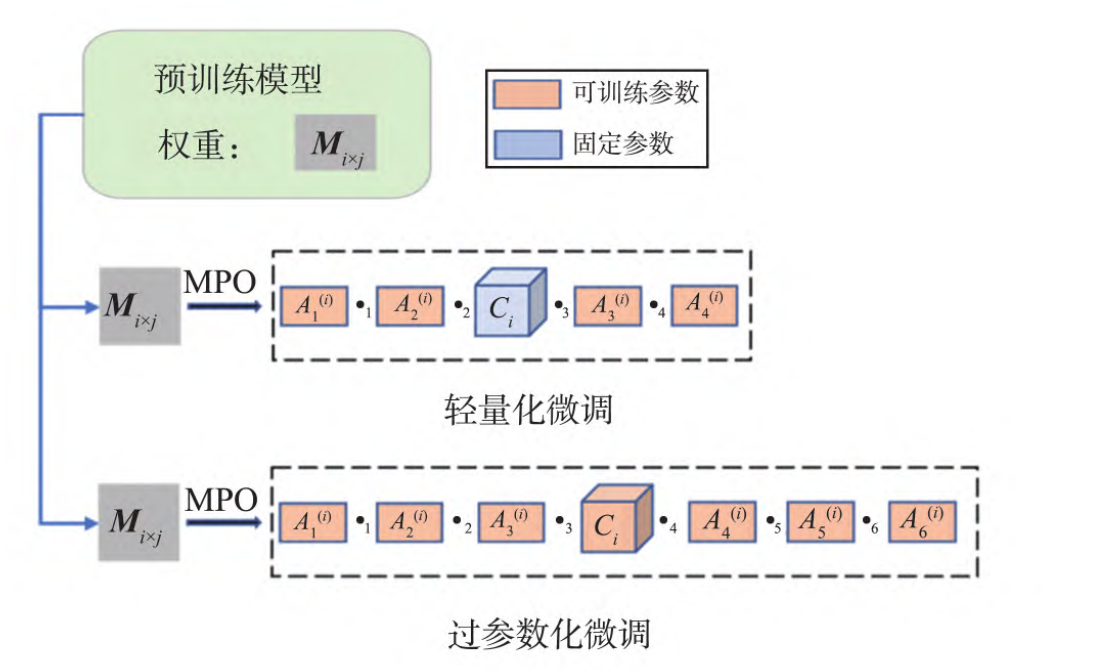
基于矩阵乘积算符表示的序列化推荐模型刘沛羽,姚博文, 高泽峰#, 赵鑫# 山东大学学报(理学版), 2024 paper / link / 推荐系统中的序列化推荐任务面临着高度复杂和多样性大的挑战,基于序列化数据的商品表示学习中广泛采用预训练和微调的方法,现有方法通常忽略了在新领域中模型微调可能会遇到的欠拟合和过拟合问题。为了应对这一问题,构建一种基于矩阵乘积算符(matrix product operator, MPO)表示的神经网络结构,并实现2种灵活的微调策略。 |
|
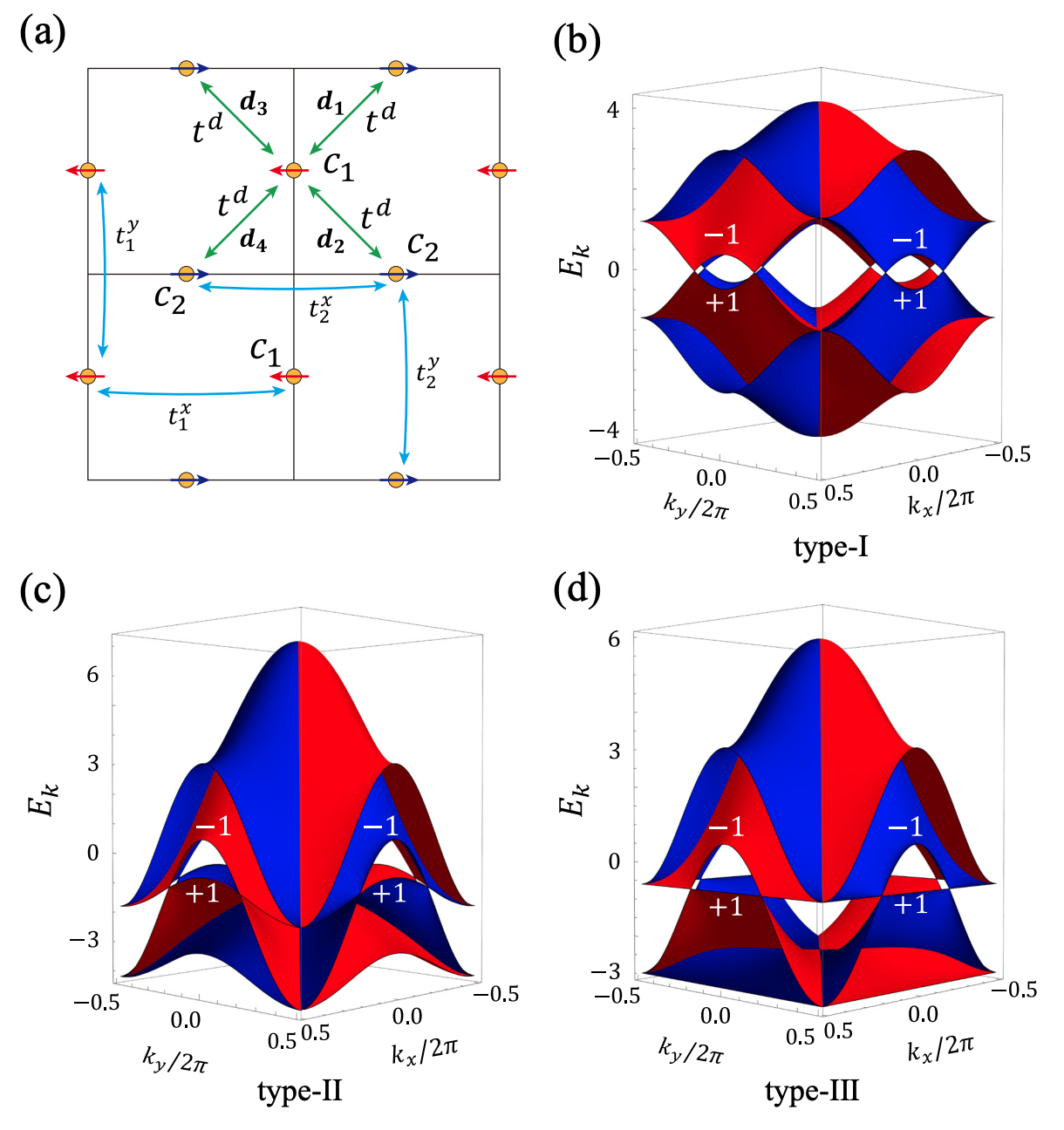
Bipolarized Weyl semimetals and quantum crystal valley Hall effect in two-dimensional altermagnetic materialsChao-Yang Tan, Ze-Feng Gao, Huan-Cheng Yang, Kai Liu, Peng-Jie Guo#, Zhong-Yi Lu# Arxiv, 2024 paper / arxiv / In this paper, we predict four ideal two-dimensional type-I altermagnetic bipolarized Weyl semimetals Fe2WTe4 and Fe2MoZ4 (Z=S,Se,Te). More significantly, we introduce the quantum crystal valley Hall effect, a phenomenon achievable in three of these materials namely Fe2WTe4, Fe2MoS4, and Fe2MoTe4, when spin-orbit coupling is considered. Furthermore, these materials have the potential to transition from a quantum crystal valley Hall phase to a Chern insulator phase under strain. |
|
Extremely strong spin-orbit coupling effect in light element altermagnetic materialsShuai Qu, Ze-Feng Gao, Hao Sun, Kai Liu, Peng-Jie Guo#, Zhong-Yi Lu# Arxiv, 2024 paper / arxiv / In this paper, we demonstrate that strong spin-orbit coupling effect can be realized in light element altermagnetic materials, and propose a mechanism for realizing the corresponding effective spin-orbit coupling. This mechanism reveals the cooperative effect of crystal symmetry, electron occupation, electronegativity, electron correlation, and intrinsic spin-orbit coupling. Our work not only promotes the understanding of light element compounds with strong spin-orbit coupling effect, but also provides an alternative for realizing light element compounds with an effective strong spin-orbit coupling. |
|
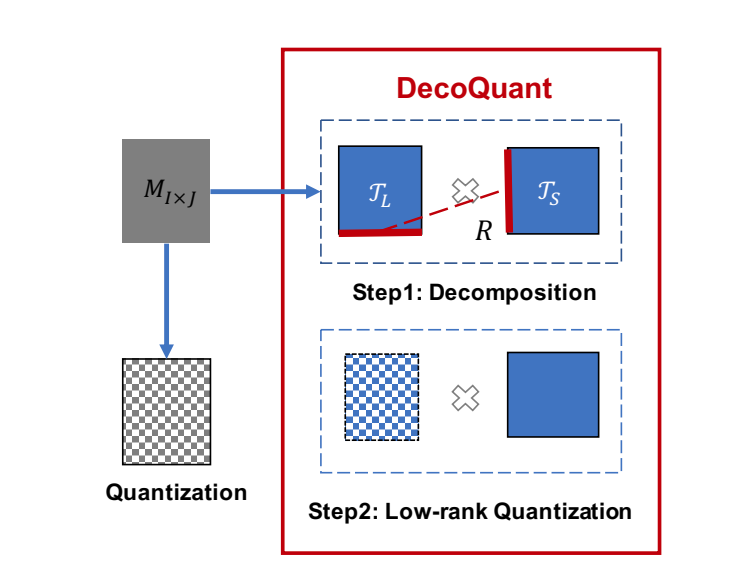
Unlocking Data-free Low-bit Quantization with Matrix Decomposition for KV Cache CompressionPeiyu Liu, Ze-Feng Gao, Wayne Xin Zhao#, Yipeng Ma, Tao Wang, Ji-Rong Wen Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL2024), 2024 paper / arxiv / link / In this paper, we introduce DecoQuant, a novel data-free low-bit quantization technique based on tensor decomposition methods, to effectively compress KV cache. Our core idea is to adjust the outlier distribution of the original matrix by performing tensor decomposition, so that the quantization difficulties are migrated from the matrix to decomposed local tensors. Specially, we find that outliers mainly concentrate on small local tensors, while large tensors tend to have a narrower value range. |
|
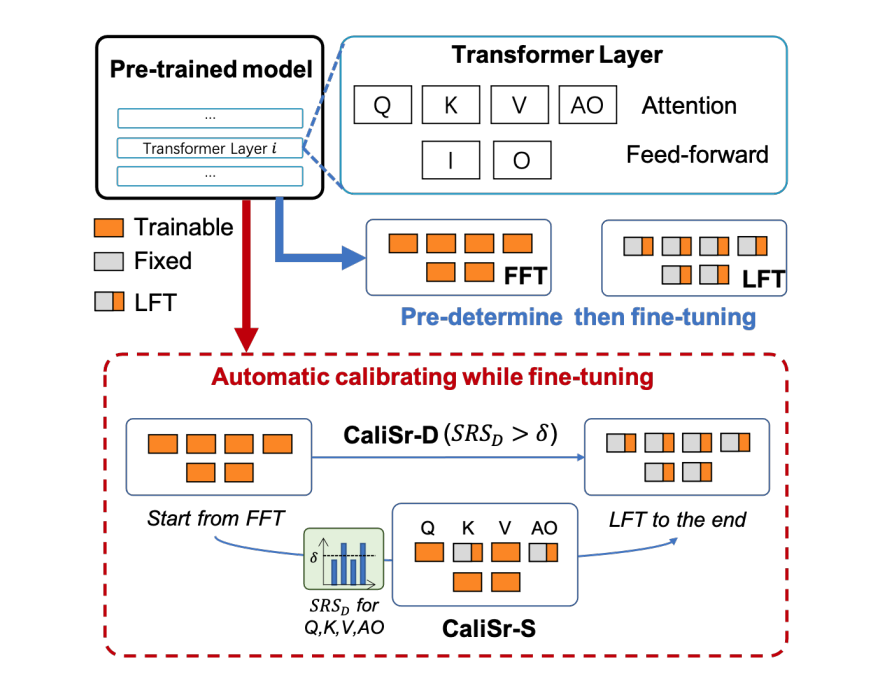
Enhancing Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning with Simple Calibration Based on Stable RankPeiyu Liu, Ze-Feng Gao, Xiao Zhang, Wayne Xin Zhao#, Ji-Rong Wen Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), 2024 paper / code / link / In this paper, we proposed both theoretical analyses and experimental verification for the proposed calibration strategy. Considering efficiency, we further propose time-aware and structure-aware strategies to determine the most crucial time to commence the fine-tuning procedure and selectively apply parameter matrices for lightweight fine-tuning, respectively. |
|
2023 |
|
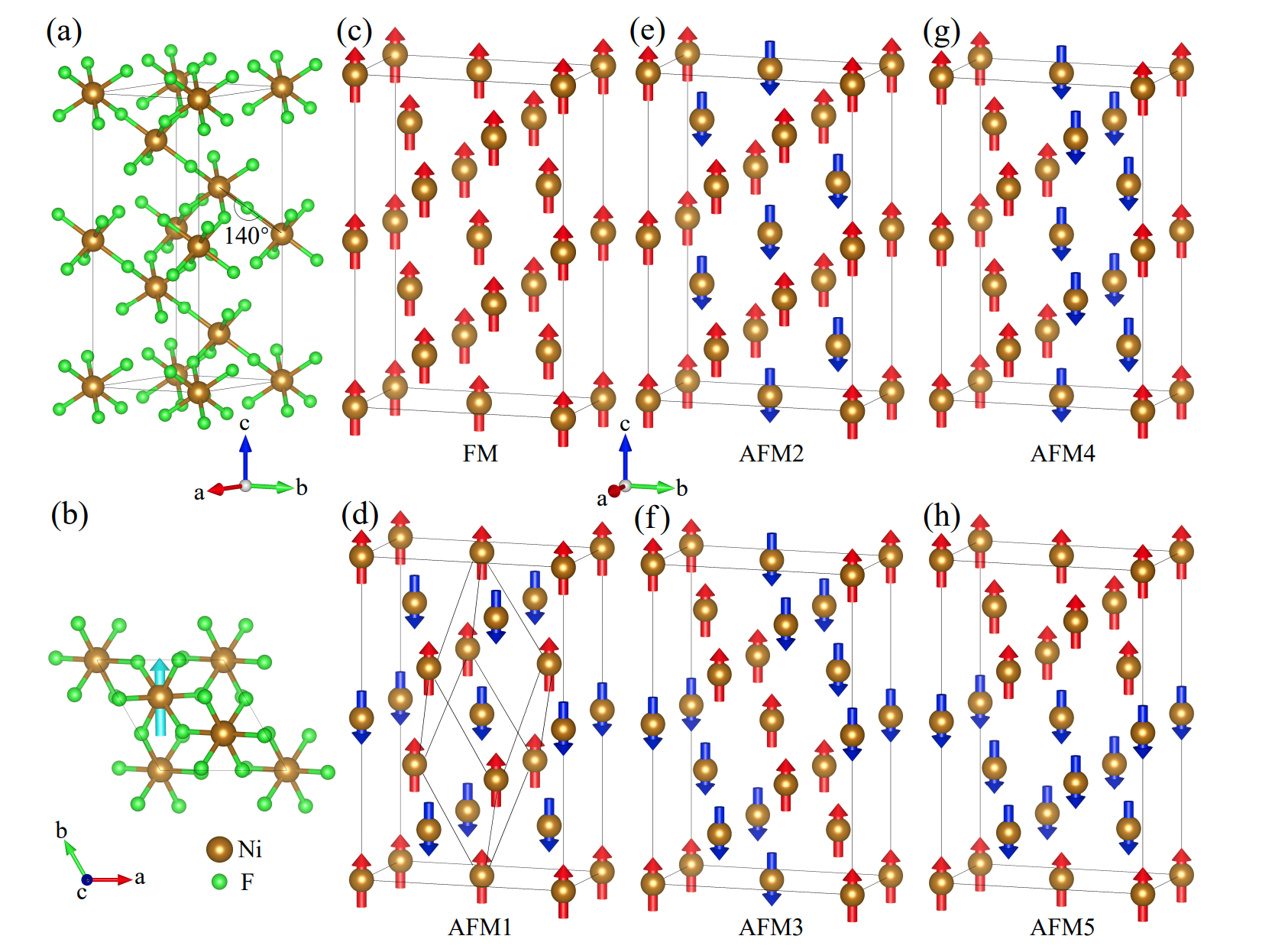
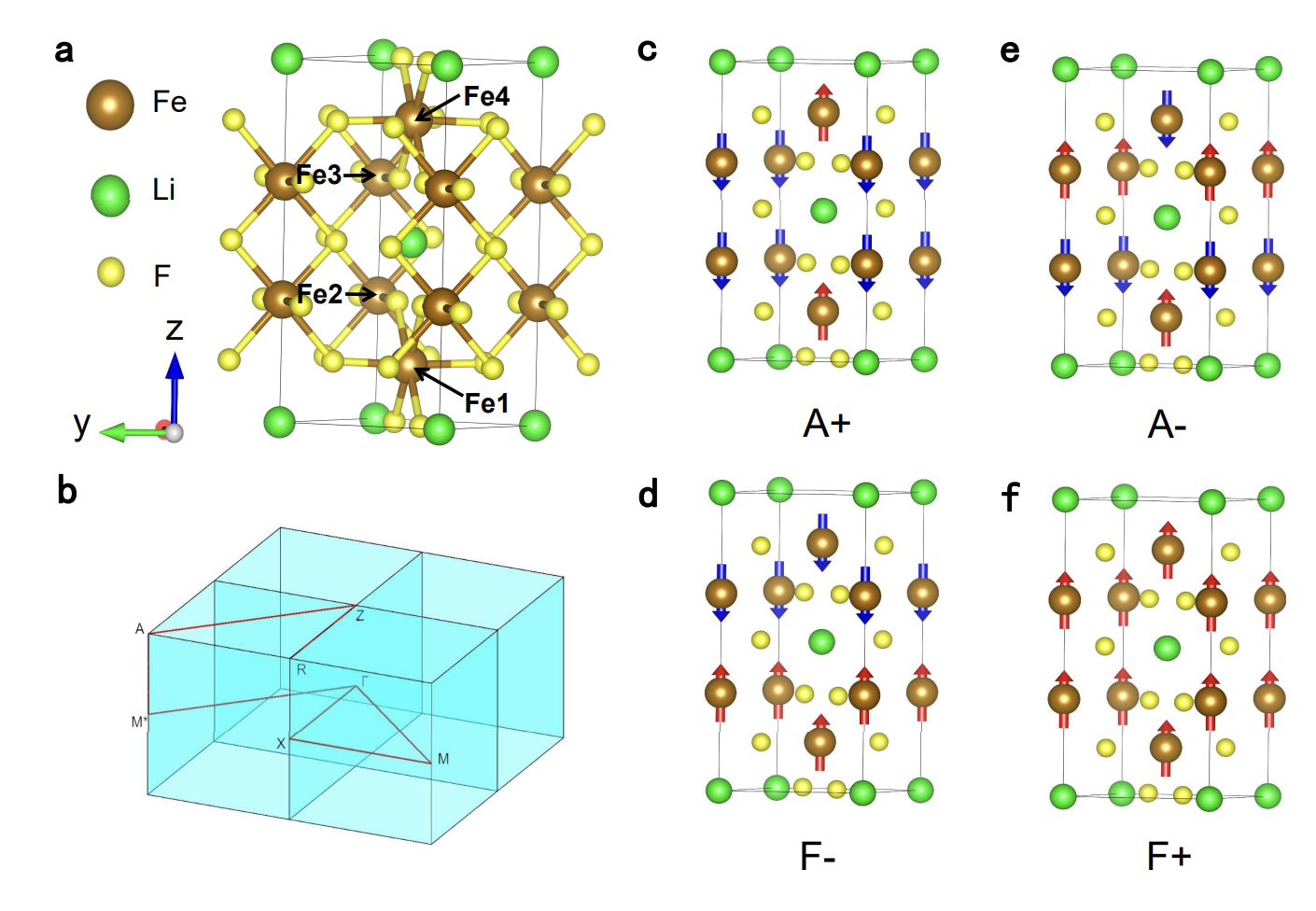
Altermagnetic ferroelectric LiFe2F6 and spin-triplet excitonic insulator phasePeng-Jie Guo, Yuhao Gu, Ze-Feng Gao, Zhong-Yi Lu# Arxiv, 2023 paper / arxiv / In this paper, we predict that LiFe2F6 is a d-wave altermagnetic and charge-ordering-mediated ferroelectric material. Moreover, the LiFe2F6 transforms into a ferrimagnetic and ferroelectric phase with strong magnetoelectric coupling under biaxial compressive strain. Interestingly, the spins of the valence band and the conduction band are opposite in ferrimagnetic LiFe2F6, which facilitates a simultaneous spin-triplet excitonic insulator phase. |
|
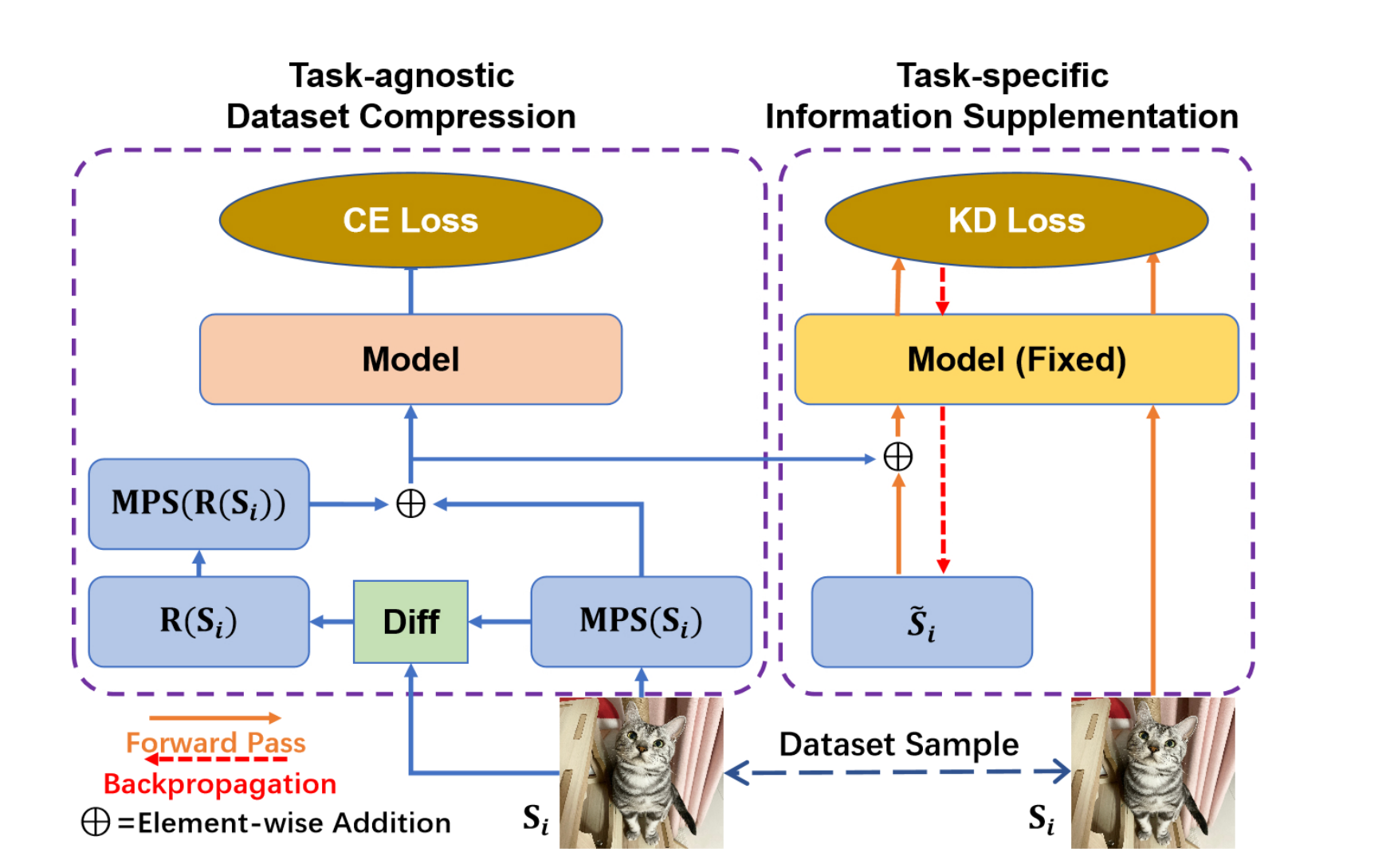
Compression Image Dataset Based on Multiple Matrix Product StatesZe-Feng Gao*, Peiyu Liu*, Wayne Xin Zhao#, Zhi-Yuan Xie, Ji-Rong Wen and Zhong-Yi Lu Future of Information and Communication Conference (FICC2024), 2023 paper / link / In this paper, we present an effective dataset compression approach based on the matrix product states (short as MPS) and knowledge distillation. MPS can decompose image samples into a sequential product of tensors to achieve task-agnostic image compression by preserving the low-rank information of the images. Based on this property, we use multiple MPS to represent the image datasets samples. Meanwhile, we also designed a task-related component based on knowledge distillation to enhance the generality of the compressed dataset. |
|
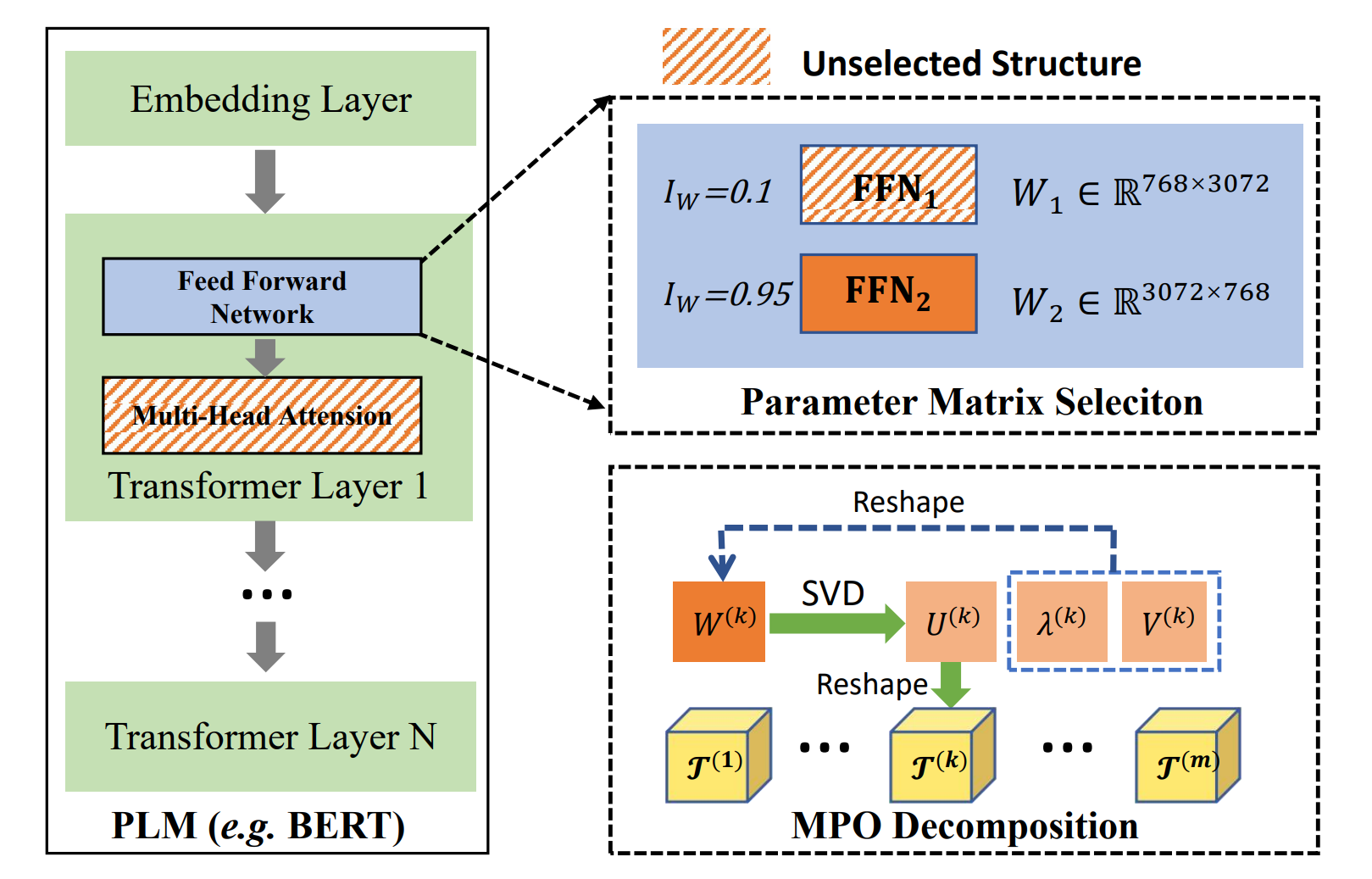
Small Pre-trained Language Models Can be Fine-tuned as Large Models via Over-ParameterizationZe-Feng Gao, Kun Zhou,Peiyu Liu, Wayne Xin Zhao#, Ji-Rong Wen Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL2023), Oral (Nominated for Best Paper Reward), 2023 paper / code / link / In this paper, we focus on just scaling up the parameters of PLMs during fine-tuning, to benefit from the over-parameterization but not increasing the inference latency. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that our approach can significantly boost the fine-tuning performance of small PLMs and even help small PLMs outperform 3x parameterized larger ones. |
|
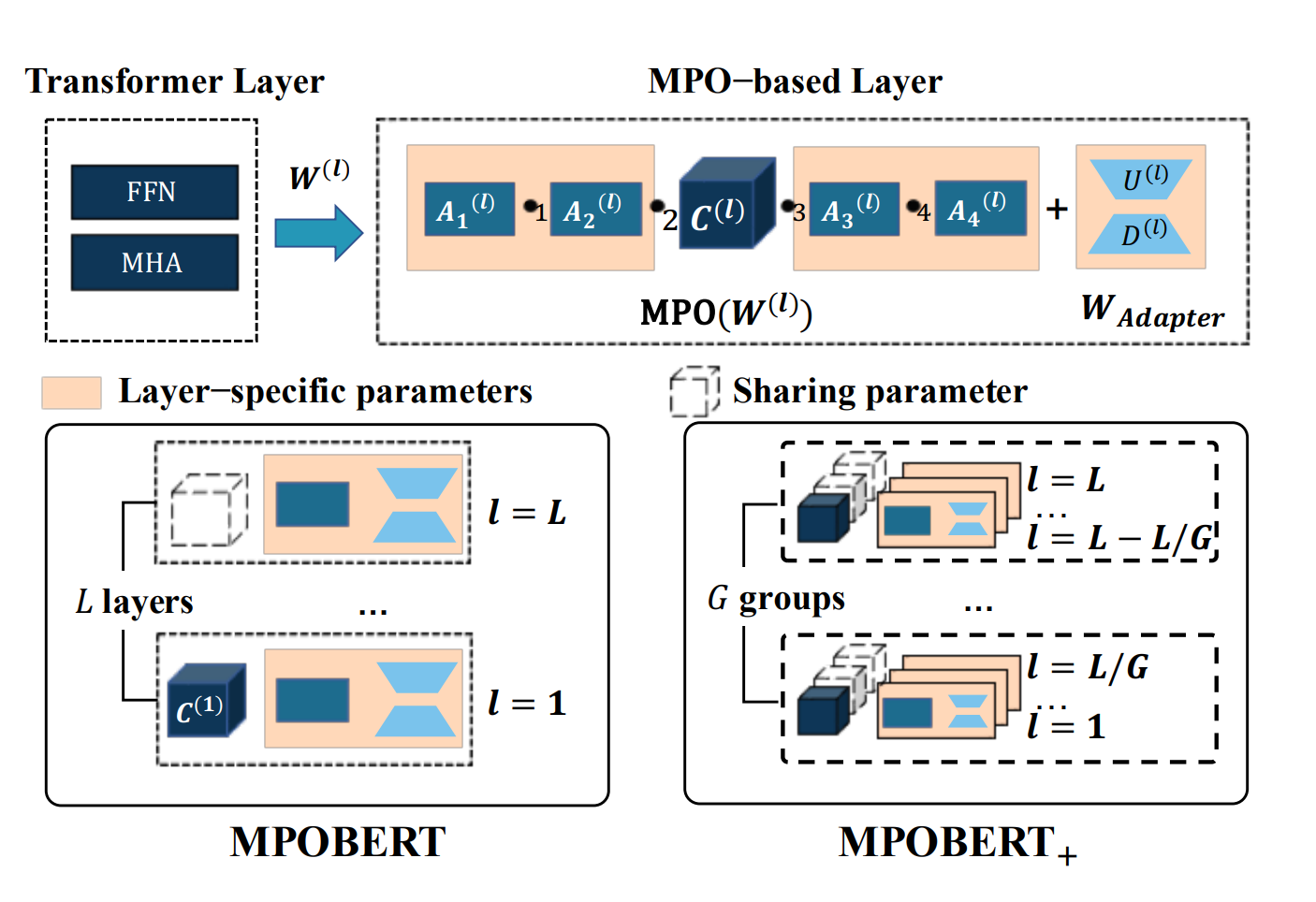
Enhancing Scalability of Pre-trained Language Models via Efficient Parameter SharingPeiyu Liu*, Ze-Feng Gao*, Yushuo Chen, Wayne Xin Zhao#, Ji-Rong Wen Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, 2023 paper / arxiv / code / link / In this paper, we propose a parameter-efficient pre-training approach that utilizes matrix decomposition and parameter-sharing strategies to scale PLMs. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed model in reducing the model size and achieving highly competitive performance (i.e. with fewer parameters than BERT-base, we successfully scale the model depth by a factor of 4x and even achieve 0.1 points higher than BERT-large for GLUE score). |
|
2022 |
|
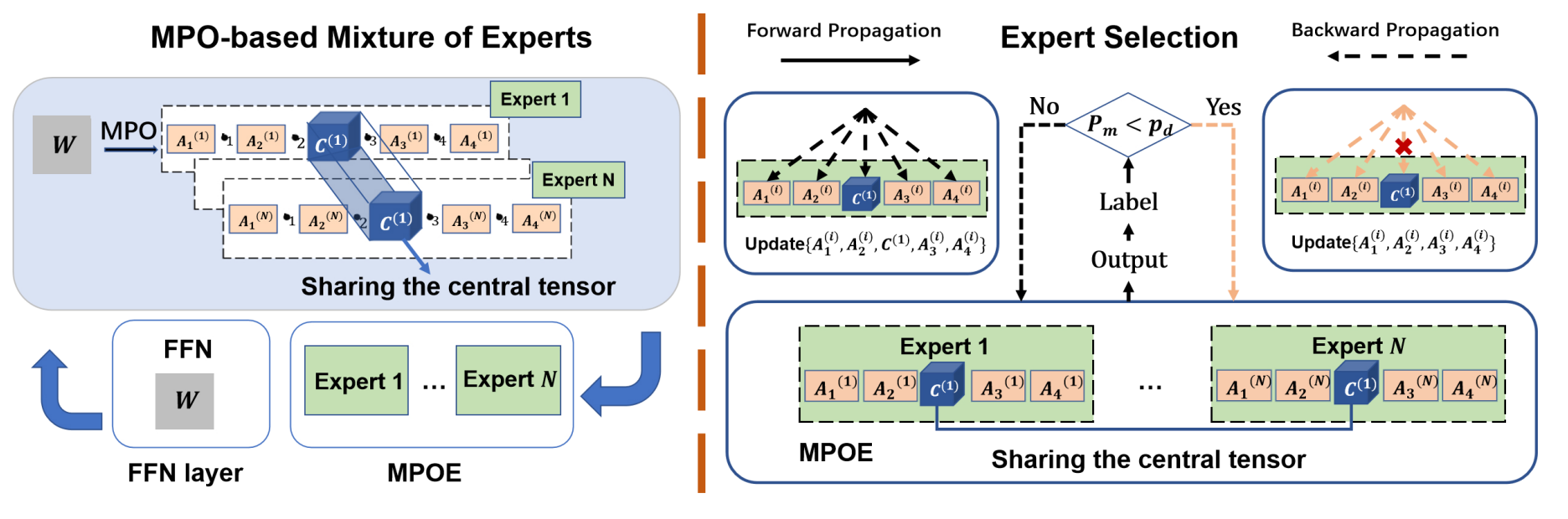
Parameter-Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Architecture for Pre-trained Language ModelsZe-Feng Gao*, Peiyu Liu*, Wayne Xin Zhao#, Zhong-Yi Lu, Ji-Rong Wen International Conference on Computational Linguistic (COLING2022), Oral Presentation, 2022 paper / arxiv / code / In this paper, we can reduce the parameters of the original MoE architecture by sharing a global central tensor across experts and keeping expert-specific auxiliary tensors. We also design the gradient mask strategy for the tensor structure of MPO to alleviate the overfitting problem. |
|
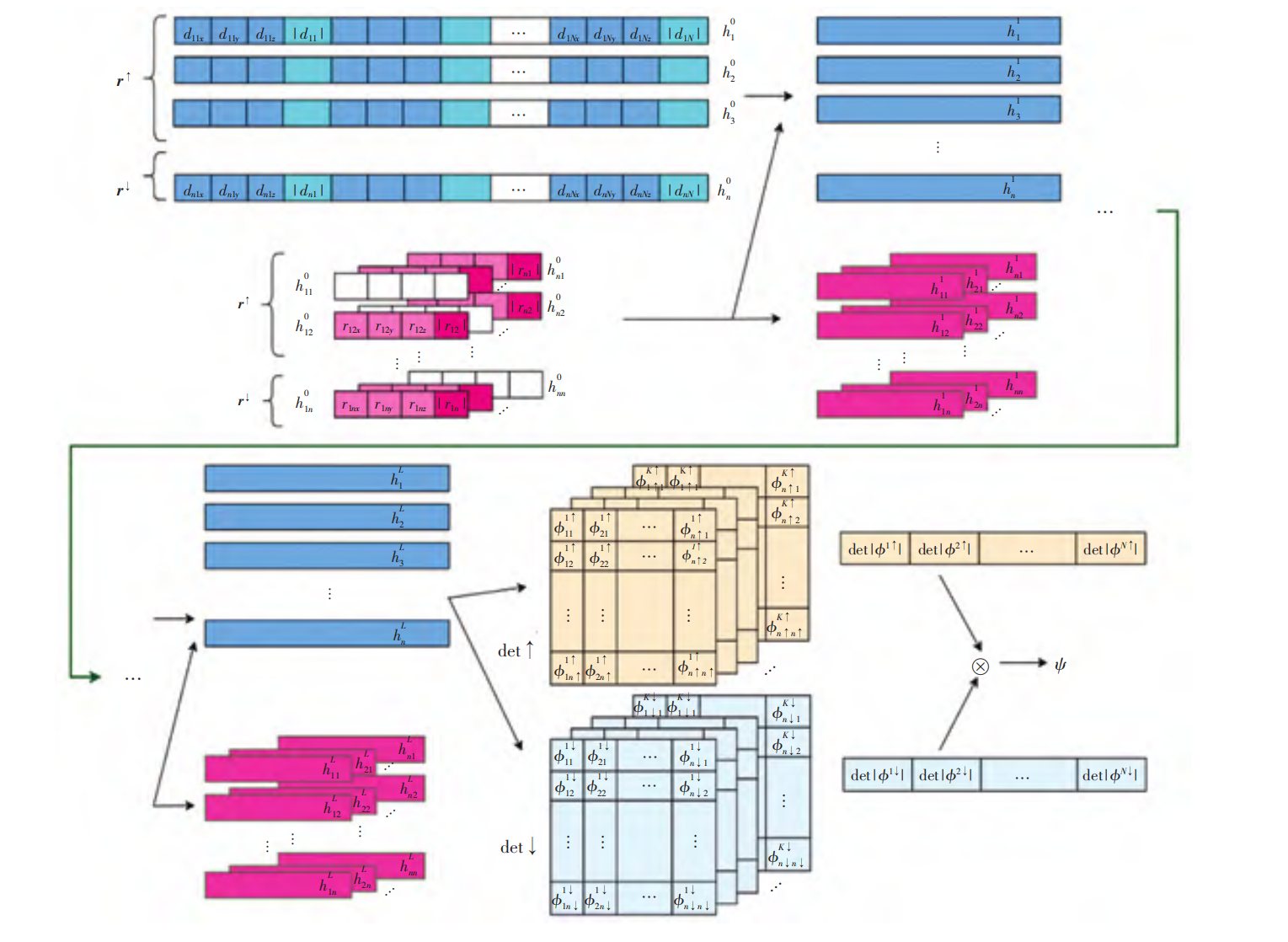
利用自注意力机制优化费米网络的数值研究王佳奇, 高泽峰#, 李永峰,王璐# 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022 paper / arxiv / 为了探索不使用特定形式的试探态研究多电子系统基态性质的方法,以至多约10个原子的小分子为例,利用神经网络的方法对多电子系统进行求解.此外,利用包含自注意力机制的Transformer结构对费米网络(FermiNet)进行改进, 结果表明:Transformer-FermiNet能够在保证原费米网络结果精度的同时将网络参数的规模缩减为原来的3/4. |
|
2021 |
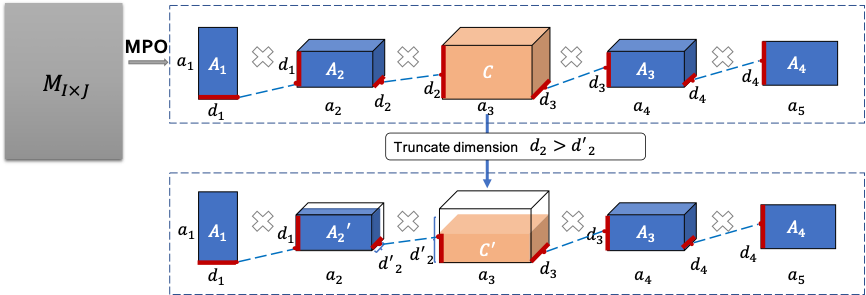
|
Enabling Lightweight Fine-tuning for Pre-trained Language Model Compression based on Matrix Product OperatorsPeiyu Liu*, Ze-Feng Gao*, Wayne Xin Zhao#, Z.Y. Xie, Zhong-Yi Lu#, Ji-Rong Wen Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL2021), Poster, 2021 paper / arxiv / code / slides / link / This paper presents a novel pre-trained language models (PLM) compression approach based on the matrix product operator (short as MPO) from quantum many-body physics. |
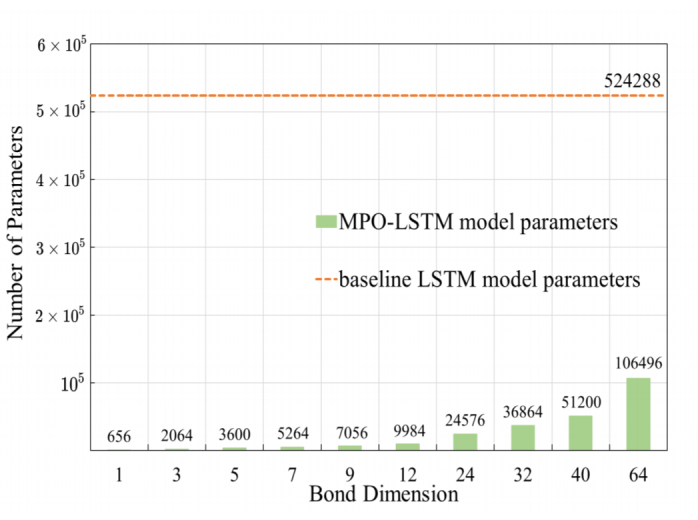
|
Compressing LSTM Networks by Matrix Product OperatorsZe-Feng Gao*, Xingwei Sun*, Lan Gao, Junfeng Li#, Zhong-Yi Lu# Arxiv, 2020 paper / arxiv / We propose an alternative LSTM model to reduce the number of parameters significantly by representing the weight parameters based on matrix product operators (MPO), which are used to characterize the local correlation in quantum states in physics. |
2020 |
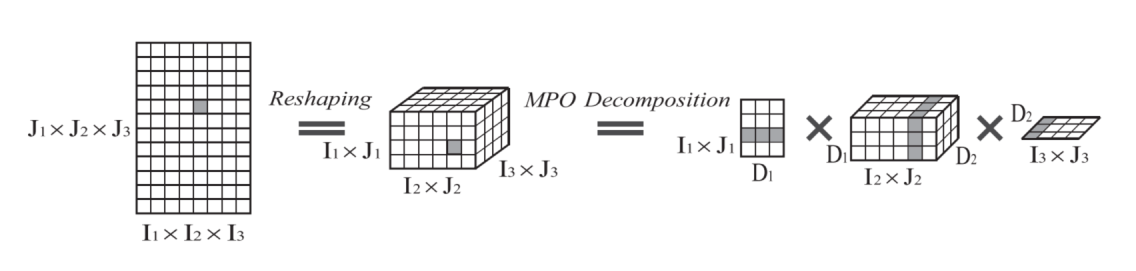
|
A Model Compression Method With Matrix Product Operators for Speech EnhancementXingwei Sun*, Ze-Feng Gao*, Zhong-Yi Lu#, Junfeng Li#, Yonghong Yan IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing 28, 2837-2847, 2020 paper / arxiv / link / In this paper, we propose a model compression method based on matrix product operators (MPO) to substantially reduce the number of parameters in DNN models for speech enhancement. |
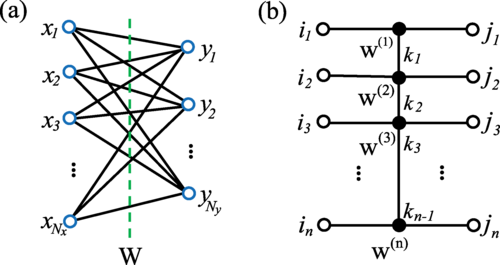
|
Compressing deep neural networks by matrix product operatorsZe-Feng Gao*,Song Cheng*, Rong-Qiang He, Zhi-Yuan Xie#, Hui-Hai Zhao#, Zhong-Yi Lu#, Tao Xiang# Physical Review Research 2 (2), 023300, 2020 paper / arxiv / code / link / In this paper, we show that neural network can be effectively solved by representing linear transformations with matrix product operators (MPOs), which is a tensor network originally proposed in physics to characterize the short-range entanglement in one-dimensional quantum states. |
* Equal contribution # Corresponding author
社会服务 |
荣誉奖励 |